ISE 2026 Entegre Sistemler Fuarındayız
Ülkü Kablo ve Feby Cable olarak ISE 2026 Entegre Sistemler Fuarı'nda olacağız

Tüm ürün gruplarımız üstün kalitede ve ileri teknoloji kullanılarak uluslararası standartlara uygun olarak üretilmektedir.
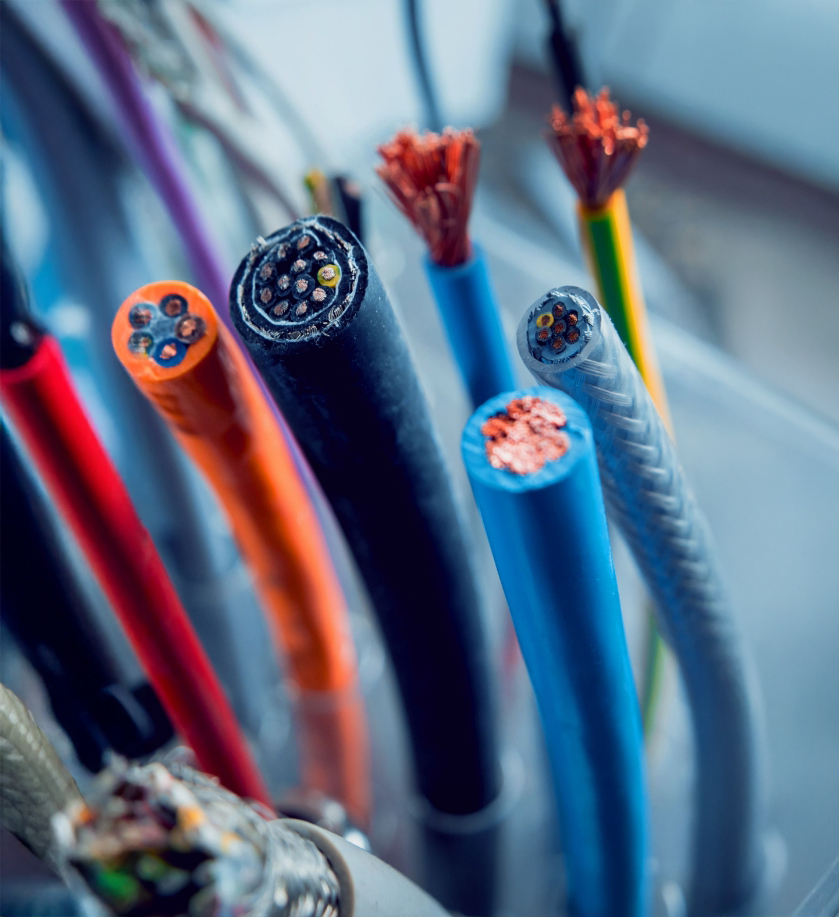





1985 yılında kablo sektörüne giren firmamız, kablo imalatında, otomotiv sektöründen elektrik elektronik sektörüne kadar birçok alandaki faaliyetlerini kesintisiz olarak sürdürmüştür.
Üretim yapısını ses kabloları, patlatma kablosu, otomotiv kabloları, yassı kablolar, tesisat kabloları, sinyal ve kontrol kabloları olarak şekillendiren firmamız, ürün çeşitliliğini sektörel taleplere uygun şekilde artırmaktadır.
Prensiplerinden şaşmadan, değişime ve gelişime açık bakış açısıyla, hedefleri doğrultusunda faaliyetlerine devam eden firmamız, sürekli yenilenen teknolojisi ve modern üretim anlayışı ile tercih edilen bir kuruluş olarak öne çıkmıştır.

Gerçek anlamda bir iş ortağı gibi davranarak, tedarikçi ve müşterilerimizin hayatlarına farklı değerler ve çözümler oluşturabilmeleri için var gücümüzle çalışıyoruz. Başarımızın sürekliliği iş ortaklarımızın büyümesi ile mümkündür. İş ortaklarımızın büyümesi için müşteri odaklı olup, ürün ve hizmet kalitesinden ödün vermeden, etik değerlere bağlı kalarak, yenilikçi ve araştırmacı yapı ile ekonomik çözümler için çalışıyoruz. Güvenilirliği ön planda tutup, şüpheden uzak, müşteri mahremiyetinin önemini bilerek çalışıyoruz.

Müşteri ziyaretleri ile kalıcı ve hızlı bir müşteri yönetim sistemi sağlanır.
ERP sistemi sayesinde müşteriye teslim edilen dokümanların büyük bir kısmı hatasız ve en kısa sürede oluşturulur.
Ürünlerimiz TSE, ISO 9001:2015 belgeleriyle onaylanmıştır. Bu nedenle ürünlerde oluşabilecek tüm olası sorunlar tespit edildiği anda çözüme kavuşturulur. Ülkü Kablo dünyanın her yerinde güvenle kullanılmaya devam ediyor.
Üretim sırasında herhangi bir sorun yaşanması durumunda üretim tekrarlanır ve hatalı ürün müşteriye gönderilmez.
Müşteri ile anlaşılan teslimat koşullarına göre teslimat aşamasında her şey en küçük ayrıntısına kadar dikkate alınır.
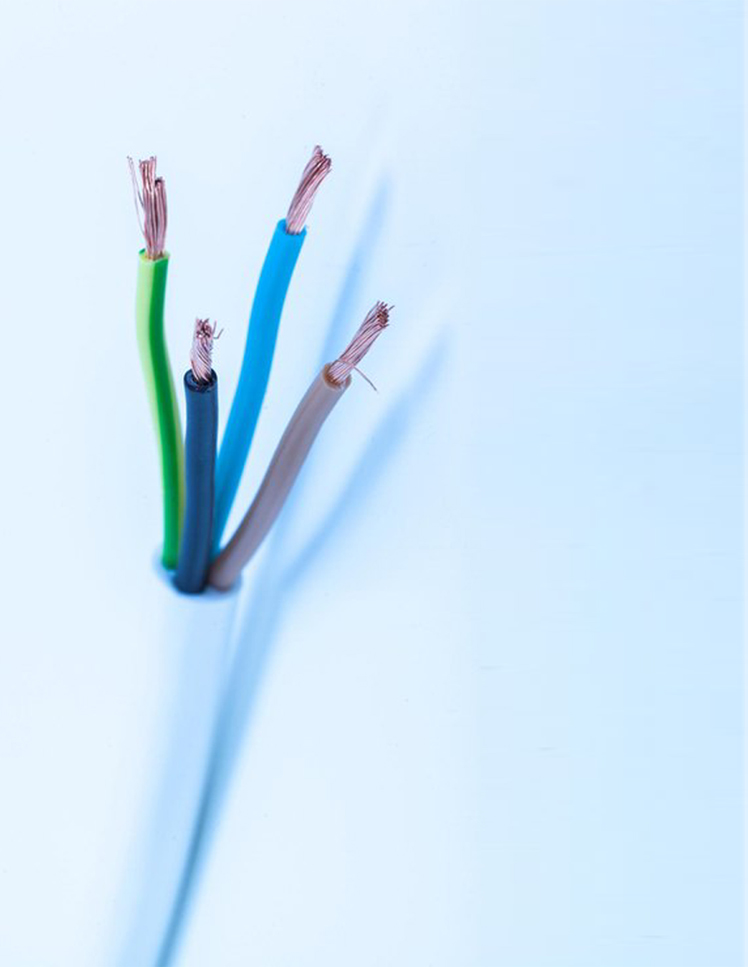


Ürünlerimiz ile ilgili detaylı bilgi almak için formu doldurarak iletişime geçebilirsiniz.
Tüm özel ürün talepleriniz için proje departmanımız ile görüşebilirsiniz.
Referanslarımız ve çalışma prensiplerimiz ile ilgili, satış departmanımız ile temas kurabilirsiniz.
Online görüşmeleriniz için Whatsapp hattımızı kullanabilirsiniz.




Ülkü Kablo ve Feby Cable olarak ISE 2026 Entegre Sistemler Fuarı'nda olacağız

Ülkü Kablo ve Feby Cable olarak ISE 2025 Entegre Sistemler Fuarı'nda olacağız.
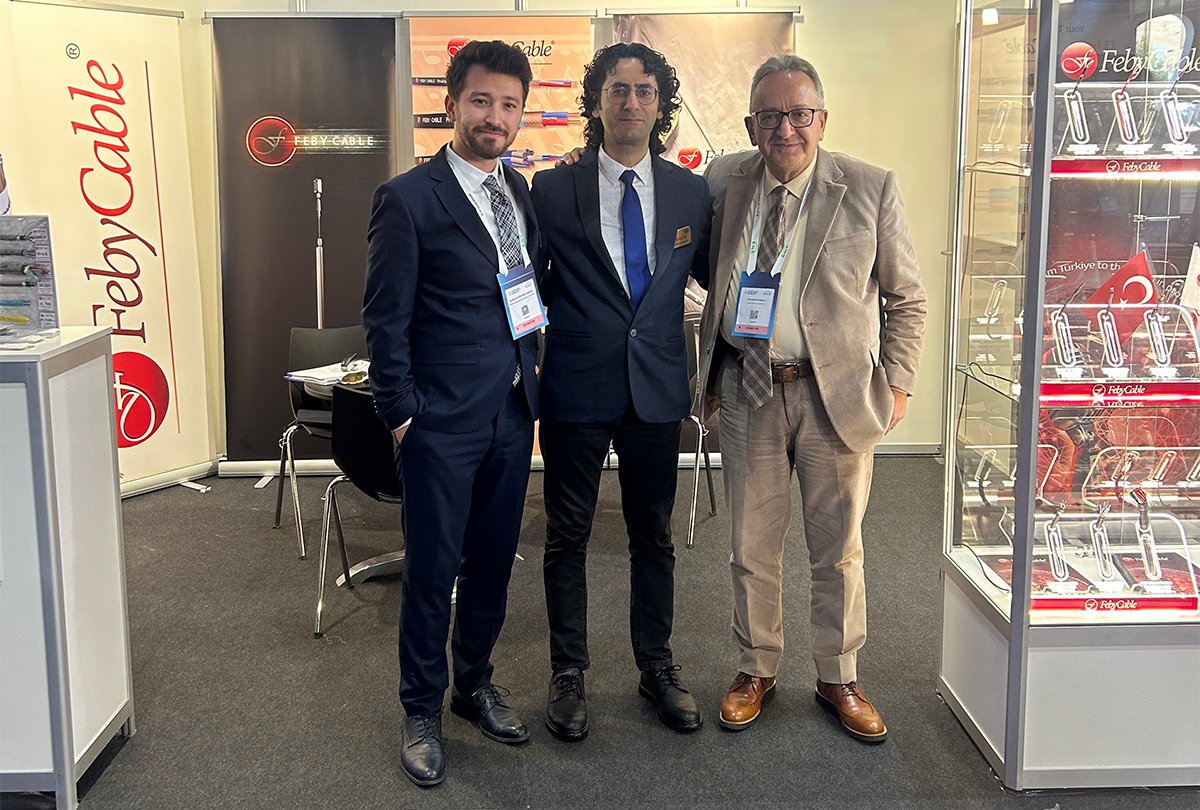

Ülkü Kablo ve Feby Cable olarak İMKB 2024 Entegre Sistemleri Avrupa Fuarı'na katıldık.